Using dedicated load balancers with RackConnect v2.0
Applies to: RackConnect v2.0
Previous section: Accessing RackConnected cloud servers
Load balancers distribute workloads across two or more servers, network
links, or other resources. This distribution maximizes throughput,
minimizes response time, and helps avoid overload. The following
information discusses several available options with dedicated load
balancers.
F5 load balancers
When you use your cloud servers to host an application that scales up
and down (for example, the web tier of an application), it is important
to have a method for adding and removing cloud servers from their
associated load balancer pools. If you use an F5 BIG-IP Local Traffic
Manager (LTM) with RackConnect, you can specify the load balancer pool
name that a cloud server should be placed in when it is created. When
you delete the cloud server, it will automatically be removed from the
pool.
With RackConnect, you can automatically associate your cloud servers with one or more load balancer pools on
your BIG-IP LTM by using one of the following options.
Metadata option
When creating a cloud server, use the metadata option to specify the pool or pools.
- Metadata Key: RackConnectLBPool
- Metadata Value: The exact name of the pool as defined on the load
balancer. Use a semicolon separated list for more than one pool.
You can specify the metadata values when you use the Cloud Servers API to create new cloud servers. View the API documentation for details
about how to use the API to enter metadata information for a cloud server.
This is the method to use if you want Auto Scale to use RackConnect with
F5 load balancers. Read more about this on the Auto Scale tips and how-to's
page about cloud bursting.
Note: If you are using next generation Cloud Servers, you can now
update a cloud server's metadata at any time to add or remove cloud servers
from load balancer pools. You can make these metadata updates by using the
Cloud Server's API.
Name match option
Before you create your cloud servers, provide
Rackspace with the preferred names and the pools to associate with
your cloud servers. Currently, you must configure this through a ticket
request to your Support team.
Requirements
Regardless of which option you select, consider the following
requirements:
-
Verify that an appropriate health check has been configured for
members of the load balancer pool or pools being used. The health
check should confirm that the website or application is fully ready
to accept end-user traffic, because the cloud server might be added
almost immediately after creation, but before your application is
ready to accept traffic, depending on the timing of the automation.
For example, it would be advisable to use a URL content check
instead of a TCP port check to confirm that a web application is
ready to accept end-user requests. -
The service port for each member of the load balancer pool must
match or the automation will not be able to determine which service
port to use. (For this same reason, there should always be at least
one member in the pool.) If a common service port cannot be
determined, a notification will be routed to your Support team for
manual intervention.
To get the name of one or more load balancer pools, contact your Support
team.
Note: Any cloud servers that were originally added to a load
balancer pool as a result of a name match rule will be automatically
removed if the respective name match rule is deleted.
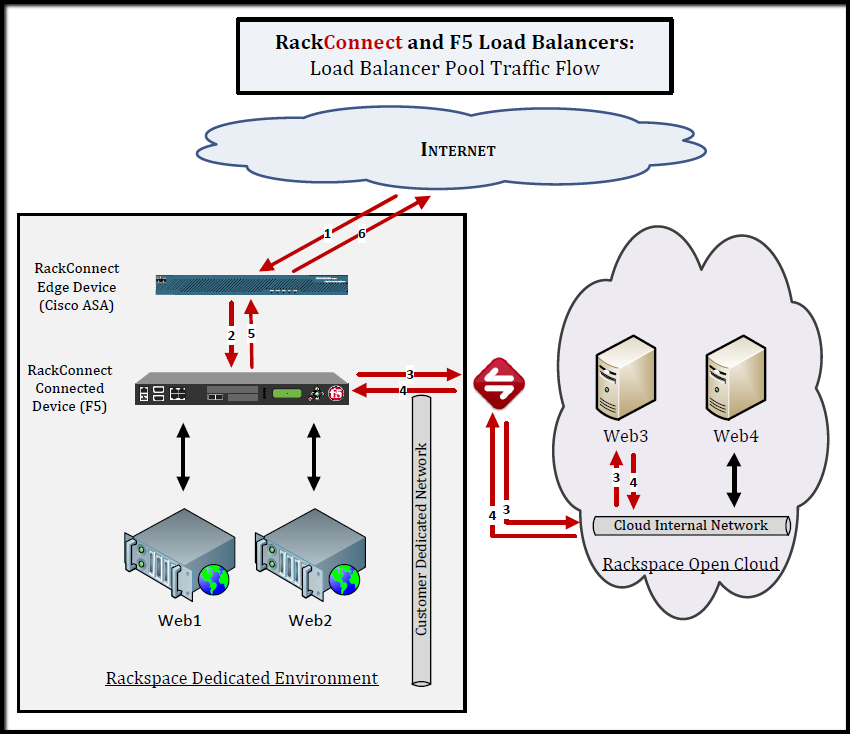
Inbound RackConnect traffic flow with an F5 load balancer
The following diagram shows the path that inbound (and return) load
balancer pool traffic follows to your cloud servers when you use an F5
BIG-IP load balancer with RackConnect:
Brocade load balancers
The Brocade ADX can also be used as a load balancer that balances
traffic between dedicated and cloud servers. In this case, the
RackConnect connected device will be a Cisco ASA firewall and any
traffic that needs to be load balanced to cloud servers will flow from
the ADX to the firewall to the cloud servers.
Benefits
The benefits of using a Brocade load balancer with RackConnect are as
follows:
-
The ability to load balance traffic between dedicated servers and
cloud servers. -
The ability to use cloud servers as sorry servers for a load
balancer pool. A sorry server normally contains a static maintenance
page that users are directed to when health checks fail for all the
members of a load balancer pool. -
The ability to maintain Client Identity (source IP persistence) to
RackConnect Cloud Servers through the use ofX-Forwardedheaders.
Your Support team can provide more details about the caveats of
client identity maintenance.
Limitations
The limitations of using a Brocade load balancer with RackConnect are
as follows:
-
Because the Brocade load balancer cannot function as a RackConnect
connected device, the RackConnect Automation feature that
automatically adds and removes cloud servers from your load balancer
pools is not available -
The Brocade load balancer must function as a full proxy for all
external requests to your cloud servers.
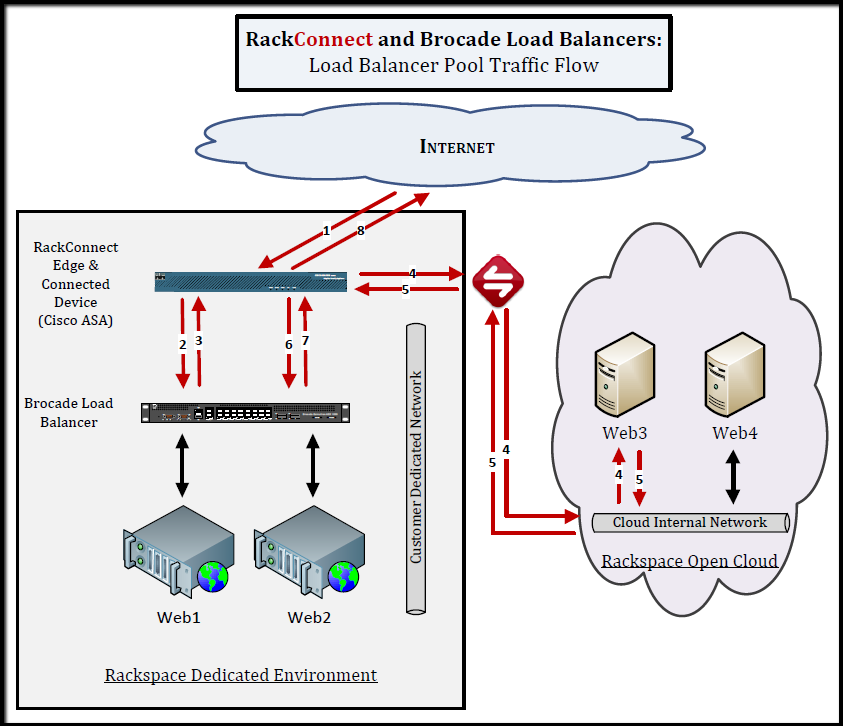
Inbound RackConnect traffic flow with a Brocade load balancer
The following diagram shows the path that inbound and return load
balancer pool traffic follows to your cloud servers when you use a
Brocade ADX load balancer with RackConnect:
If you have any questions about using Dedicated load balancers with
RackConnect, contact your Support team.
Next section
Updated 2 months ago