Manage OnMetal Cloud Servers through the API
You can use OnMetal Cloud Servers to start bare metal servers by using the Rackspace Cloud Servers API. Follow these steps to set up an OnMetal server through the API.
Note: For the parallel steps in the Cloud Control Panel, see Create OnMetal Cloud Servers.
Set up the API client
Follow these steps to create your OnMetal server through the API, if you don't already have an OpenStack Nova API client set up.
-
Install supernova and rackspace-novaclient via pip:
pip install supernova rackspace-novaclient -
After you have access to OnMetal, configure
supernovato work with the Rackspace IAD region by adding the following information to ~/.supernova:[iad] OS_AUTH_URL=https://identity.api.rackspacecloud.com/v2.0/ OS_USERNAME=< Your Rackspace Username > OS_PASSWORD=< Your Rackspace API Key > OS_TENANT_NAME=< Your Rackspace Tenant ID> OS_AUTH_SYSTEM=rackspace OS_REGION_NAME=IAD NOVA_SERVICE_NAME=cloudServersOpenStack
Note: Be sure to set the appropriate values for the following parameters:
- OS_USERNAME: Your Rackspace Cloud username, which is the user name you use to log in to the Cloud Control Panel.
- OS_PASSWORD: Your Rackspace Cloud API key, which you can access in the Cloud Control Panel by clicking Account:userName > Account Settings.
- OS_TENANT_NAME: Your Rackspace Cloud tenant ID, which displays as your Account number in the username menu of the Cloud Control Panel.
IMPORTANT: Use a Secure Shell (SSH) key pair to create OnMetal servers. Ignore the administrator password returned by the create server operation because it does not allow access to the OnMetal server. For information about generating SSH Keys, see Manage SSH Key Pairs for Cloud Servers with python-novaclient.
Upload an SSH key pair
OnMetal servers only allow an SSH key pair based login, and they do not support password-based login. Use the
following command syntax to upload your SSH key pair:
supernova iad keypair-add -pub-key <path to your public key> <public key name>For example:
supernova iad keypair-add --pub-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub RussellFor information on generating SSH key pairs, see Manage SSH Key Pairs for Cloud Servers with python-novaclient.
Start your server
To start your OnMetal server, choose an operating system (image) and a server size (flavor).
Supported Images
- OnMetal - CentOS® 7
- OnMetal - CentOS 6.5
Note: Run the CentOS 6.5 image only on a Linux® Kernel release of 3.10 or higher, to avoid performance degradation. - OnMetal - Debian 7® (Wheezy)
Note: Rackspace adds other operating system images when they are ready.
Supported Flavors
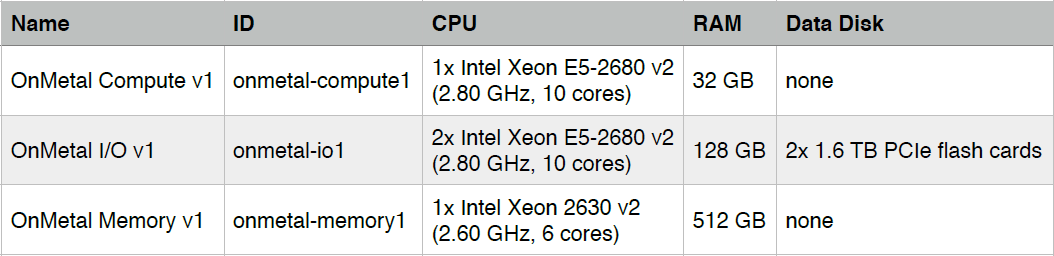
- All flavors have a 32 GB system disk.
- All flavors include dual 10 GigE NICs in a high availability bonded configuration and use VLAN tagging to access ServiceNet (for traffic within a Rackspace region) and PublicNet (the Internet).
Run the boot command
Use the following command to start (boot) your OnMetal server:
supernova iad boot --flavor <flavor ID> --image <image ID> --key-name <key name>
<server name>For example:
supernova iad boot --flavor onmetal-compute1 --image 1387253c-7735-4542-9612-26bc9ff77a9d --key-name johndoe onmetal-test
You should see output similar to the following example:
+------------------------+--------------------------------------+
| Property | Value |
+------------------------+--------------------------------------+
| status | BUILD |
| updated | 2014-05-31T00:23:29Z |
| OS-EXT-STS:task_state | scheduling |
| key_name | johndoe |
| image | OnMetal - Debian 7 (Wheezy) |
| hostId | |
| OS-EXT-STS:vm_state | building |
| flavor | OnMetal I/O v1 |
| id | a8ea2366-9e50-4604-b6ce-e3edb8750451 |
| user_id | 83362 |
| name | teeth5 |
| adminPass | 6FgtaEqkapRo |
| tenant_id | 545251 |
| created | 2014-05-31T00:23:29Z |
| OS-DCF:diskConfig | MANUAL |
| accessIPv4 | |
| accessIPv6 | |
| progress | 0 |
| OS-EXT-STS:power_state | 0 |
| config_drive | |
| metadata | {} |
+------------------------+--------------------------------------+Note: Although this output displays an administrator password, this password is not actually used. You can safely ignore it. The server takes about five minutes to build. Check the status by running the following command:
supernova iad show <instance id>The output should look similar to the following example:
+------------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Property | Value |
+------------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+
| status | ACTIVE |
| updated | 2014-05-31T00:27:34Z |
| OS-EXT-STS:task_state | None |
| private network | 10.184.0.48 |
| key_name | johndoe |
| image | OnMetal - Debian 7 (Wheezy) (1387253c-7735-4542-9612-26bc9ff77a9d) |
| hostId | 8a12611e45a1e15a1aec221ab05c8494524d6bf00e7fb17c5c82722a |
| OS-EXT-STS:vm_state | active |
| public network | 23.253.157.48 |
| flavor | OnMetal I/O v1 (onmetal-io1) |
| id | a8ea2366-9e50-4604-b6ce-e3edb8750451 |
| user_id | 83362 |
| name | teeth5 |
| created | 2014-05-31T00:23:29Z |
| tenant_id | 545251 |
| OS-DCF:diskConfig | MANUAL |
| accessIPv4 | 23.253.157.48 |
| accessIPv6 | |
| progress | 0 |
| OS-EXT-STS:power_state | 1 |
| config_drive | |
| metadata | {} |
+------------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+After a few minutes, the server is assigned a public and private IP address. You can see them in the output of the show command. After the status becomes ACTIVE, the server boots for the first time. The server isn't reachable, until after a few minutes, when the network configuration is complete.
Log in to the server
After the server starts, use the SSH key pair that you specified to log in to the server:
Note: The default user on Debian® and CentOS® is root.
ssh root@<publicIPaddress>Delete the server
If you need to, you can also delete or cancel the server following these commands:
-
Execute the following command, replacing the example ID with your server's ID:
supernova iad delete a8ea2366-9e50-4604-b6ce-e3edb8750451 -
Use the following command to see the progress.
supernova iad listYou should see output similar to the following example:
+--------------------------------------+---------+--------+------------+-------------+---------------------------------------------+ | ID | Name | Status | Task State | Power State | Networks | +--------------------------------------+---------+--------+------------+-------------+---------------------------------------------+ | d1d58868-2b14-4fa5-b01f-e51d658556a8 | highcpu | ACTIVE | deleting | Running | public=23.253.157.105; private=10.184.0.105 | +--------------------------------------+---------+--------+------------+-------------+---------------------------------------------+
Note: Your server goes into the task state deleting. OnMetal server deletions take longer than virtual server deletions, usually a few minutes.
Using OnMetal
The flashcards included with the OnMetal I/O flavor are unformatted, but you can format them. For more information, see Configure flash drives in High I/O instances as Data drives.
Updated about 2 months ago
