Identifying suspicious email
This article describes how Rackspace Email Webmail identifies suspicious emails.
Prerequisites
- Applies to: Administrator and User
- Difficulty: Easy
- Tools required: Webmail Access
Identify suspicious email
Suspicious email is a gray area between legitimate email and spam. Webmail employs Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) indicators to determine if an email is suspicious. There are several other items you can see that indicate if an email is legitimate. These indicators are simple but are extremely valuable in determining the validity of a message.
Messages that are deemed suspicious show a yellow warning banner in Webmail’s preview pane. The intent of this banner is to encourage you to confirm the legitimacy of the sender and the contents of the message before clicking on any links, downloading any attachments, or replying.

Webmail clearly shows the display name and email address of the sender. Comparing the display name to the email address is a simple way to check for display name spoofing. Display name spoofing is when bad guys place a name that you recognize in the From address, such as the name of your manager, but the associated email address is not for that person. For example, Webmail shows you "From: John Doe <[email protected]>". Assuming John Doe is your manager’s name, <[email protected]> is definitely not your manager’s email address.
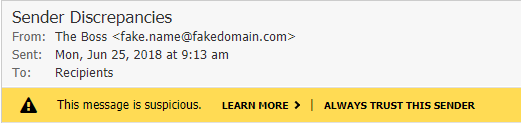
Webmail shows you if the domain of the sender does not match the domain used to send the message. The domain that sent the message is represented by the 'sent from' added to the sender's address. In some cases, this situation is normal for sending services that are used for marketing and sales campaigns, newsletters, and similar email distributions. However, it can also be an indication of spoofing. Building on the previous example, if the same bad guy compromised a Gmail mailbox and is sending email pretending to be your manager, it appears in Webmail as "From: John Doe <[email protected]> sent from gmail.com". Assuming your manager never uses Gmail for work purposes, this is a clear indicator that the message is suspicious.
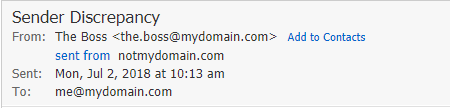
To report suspicious email as spam, you can drag the message to the Spam folder, or you can click Report Spam in the More menu.
Remember, it is always a best to verify any request for personal information or money that is received via email. For more information about how to recognize phishing emails, visit our blog at https://blog.rackspace.com/email-phishing-rise-mailbox-safe.
Updated over 1 year ago
