Building servers without PublicNet or ServiceNet¶
If a server is built without a PublicNet or ServiceNet network, it cannot access certain Rackspace products and services. However, it is possible to access some of these products (and the Internet) indirectly by using a Gateway Instance.
In the diagram below, the web server and database server do not have PublicNet attached. Instead, their outbound Internet access is routed through the Gateway Instance by using Cloud Networks. The web server also has public-facing services exposed by using a Cloud Load Balancer, which connects over ServiceNet.
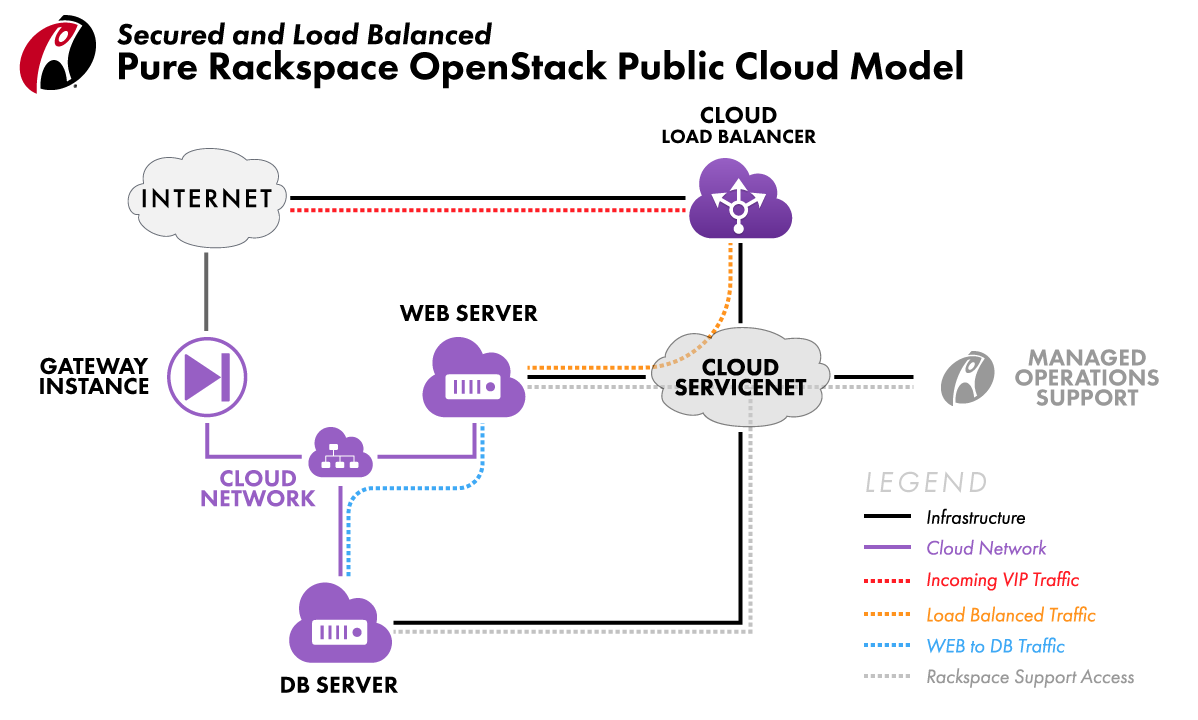
PublicNet provides a server with direct access to the Internet.
ServiceNet provides a server with access to Cloud Databases, Cloud Load Balancers, Cloud Files, Cloud Backup, Managed Cloud Support, and Windows activation. This network is required for all Managed Operations customers.
Cloud Networks provides single-tenant, inter-server communication and can provide indirect Internet access by using a Gateway Instance.
How to manually set up Internet access for servers without PublicNet¶
For added security, you may opt to build servers without PublicNet and/or ServiceNet.
Note
It’s much easier to build a Gateway Instance which performs all the steps below automatically.
1) Create a Cloud Network with the Neutron API or via the neutron CLI. You cannot create the network by using the Cloud Control Panel.
2) Within the Cloud Network you just created, create a subnet including the following information:
IP version: We use version 4 in these examples, but version 6 will work. Only one IP version (4 or 6) may be created per Cloud Network.
Gateway IP: We recommend specifying the first available IP in your network range, such as ‘.1’ for a /24 network.
DNS servers: We recommend using the Rackspace DNS servers. Check the DNS configuration of your Cloud Servers to find the Rackspace DNS server IPs. Note that these vary per region.
Allocation pool start and end: This is the pool of IPs that are assigned to any servers that you build in the network. Do not include the gateway IP in this allocation pool because you can’t assign the gateway IP manually if it’s in the allocation pool. To be safe, we recommend marking the 9th available IP as the start of the allocation pool. That allows you to manually assign the first 8 IPs in the range as needed.
(Optional) host routes: These are additional static routes that are included in the routing table of any server connected to this subnet. Typically they are only needed when a VPN endpoint is a different host than the default gateway.
3) Create a fixed IP port with the Gateway IP that you specified in the previous step.
4) Build a Gateway Instance with PublicNet, and the fixed IP port that you created in the previous step. (ServiceNet is optional.)
5) Configure NAT and routing on the Gateway Instance. Consult your OS distributor’s documentation as necessary.
6) To test routing, build a server with the Cloud Network attached, but without PublicNet. (ServiceNet is optional.) Via the emergency console or ServiceNet, log in and verify that Internet access works. If it does not, verify your previous steps.
See also
Understanding Cloud Networks introduces key ideas. To learn how to put these ideas to work, start at Actions for Cloud Networks.