Cloud Networks - Neutron API v2.0#
Last updated: Aug 21, 2023
To use the information provided here, you should have a general understanding of the service and have access to an installation of it. You should also be familiar with the following technologies:
RESTful web services
HTTP/1.1
JSON serialization formats
Use the following links to jump directly to user and reference information for the Cloud Networks service REST API:
Note
You can also use Cloud Networks from the Cloud Control Panel.
The Rackspace Cloud Networks service enables customers to perform the following tasks:
List networks to which the specified tenant has access.
Create isolated networks.
Show details for isolated networks.
Delete an isolated network, if it is not associated with any server.
Note
To detach a network from a server, you must use the Cloud Networks virtual interface extension to delete the virtual interface for the network from the server. For more information, see Delete virtual interface.
Manage subnets.
Manage ports.
Manage security groups and security group rules.
Manage and share IP addresses between servers in the same public zone.
Networking: Neutron versus Nova-Network#
Rackspace first introduced networking services that were based on the OpenStack Nova-Network API and exposed these services via the /os-networksv2 Cloud Servers extension. For documentation on these operations, see Network extension. This version of the service is now superseded by the current networking API, based on OpenStack Neutron, which offers a richer suite of networking services. Both APIs continue to function, but the Neutron API will be the base for all the future networking services that Rackspace offers. We recommend that you use the Neutron API for your Cloud Networks API operations.
The current API introduces three new top-level resources — /networks,
/ports, and /subnets — which are included in the OpenStack Neutron API.
All new networking services that we offer will make use of these resources and
build on the OpenStack Neutron API to help you build rich networking topologies
and configure advanced network services.
As part of the new API, the following new capabilities are available to users:
Create and manage isolated networks using the new API
Assign routes to cloud servers at boot-time (host routes)
Specify allocation pools to subnets (CIDRs) on isolated networks to control the IP address assignment on your cloud servers
Allocate an IP address of your choice to ports on isolated Networks
Dual-stack isolated networks: Allocate both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses on the same isolated network port.
For guidance on the Nova-Network API networking operations, see the Network section.
Rackspace public cloud networks#
The Rackspace Public Cloud enables you to attach one or more of the following networks to your server:
Public (PublicNet)#
Rackspace PublicNet connects the cloud infrastructure components (like servers, load balancers, and network appliances) to the Internet. PublicNet is optimized for north-south traffic (traffic flowing to and from the Internet). It follows a direct addressing model, so that all public IP addresses are directly configured on the servers without using Network Address Translation (NAT). PublicNet is dual-stacked for IPv4 and IPv6. When you create servers with PublicNet, your servers get an IPv4 and an IPv6 address by default.
When you list networks, PublicNet is labeled public.
Service (ServiceNet)#
ServiceNet is an internal, IPv4-only multi-tenant network within each Rackspace
Cloud region that is optimized to carry east-west traffic. It provides
servers access to regional services such as Cloud Files, Cloud Load Balancers,
Cloud Databases, and Cloud Backup at no cost. ServiceNet is also required for
Windows Cloud Server activation. We recommend that you connect servers to
ServiceNet so that they can access these services. The networks
10.176.0.0/12 and 10.208.0.0/12 are reserved for ServiceNet.
When you list networks, ServiceNet is labeled private.
Isolated networks (Cloud Networks)#
Isolated networks are user-defined L2 networks that are fully isolated and single-tenant, and offer users a means to securely connect their application servers. They are provided at no charge. Isolated Networks can now be provisioned either as IPv4 or IPv6, or they can be dual stacked (IPv4 and IPv6). Isolated networks are recommended for all inter-server communication. Even though ServiceNet can also be used for server east-west (backend) connectivity, ServiceNet is not recommended for that purpose because, unlike isolated networks, ServiceNet is multi-tenant. Isolated networks also include full support for the broadcasting and multicasting required for some clustering technologies.
Networks attached during server provisioning#
Which networks get attached, manually or automatically, to a newly provisioned server depends on which of the following methods you use to provision that server:
Nova boot command: You must specify the networks that you want to attach to your server. The UUID for ServiceNet is
11111111-1111-1111-1111-111111111111and the UUID for PublicNet is00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000. If you do not specify any networks, ServiceNet and PublicNet are attached by default. To attach to isolated networks that you have created, in addition to PublicNet and ServiceNet, you must explicitly specify them in the command.Cloud Control Panel: PublicNet and ServiceNet are automatically attached, but you can disable these networks during the server creation process. You can also attach any isolated networks that you have created.
Note
You can explicitly opt out of attaching to the Rackspace networks, which introduces certain potential complications. For more information, see Consequences of detaching from Rackspace networks.
Consequences of detaching from Rackspace networks#
When you provision a cloud server, you can attach to one or more isolated networks and the Rackspace networks. You can also explicitly opt out of attaching the Rackspace networks to the server, which introduces the following consequences:
If you do not attach the PublicNet network to the server, the server cannot access the Internet and some Rackspace products and services.
If you do not attach the ServiceNet network to the server, the server cannot access certain Rackspace products and services.
The following graphic depicts the services that are available only when you attach the Rackspace networks to your server:
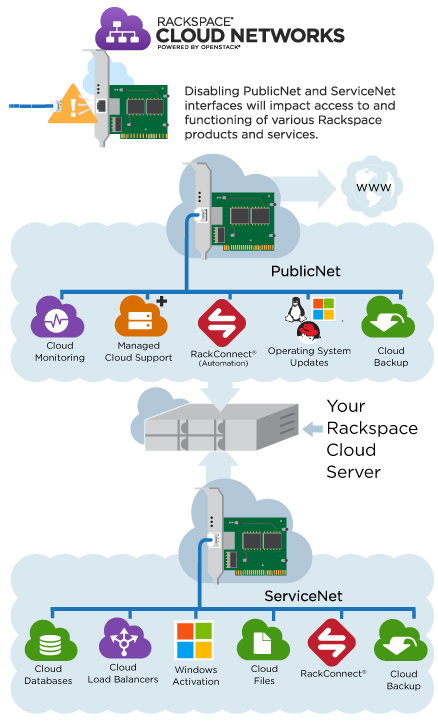
Opting out#
To opt out of attaching the Rackspace networks to your server, perform the following action depending on how you are provisioning the server:
nova boot command: Specify the optional –no-public and –no-service-net parameters.
Cloud Servers Nova-Network API (nova client or cURL): If you do not specify any networks, ServiceNet and PublicNet are attached by default. However, if you specify an isolated network, you must explicitly specify the UUIDs for PublicNet and ServiceNet to attach these networks to your server.
The UUID for ServiceNet is
11111111-1111-1111-1111-111111111111and the UUID for PublicNet is00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000.Omit these UUIDs from the request to opt out of attaching to these networks.
Cloud Control Panel: Clear the PublicNet and ServiceNet selections during the server creation process. You are warned that your capabilities might be degraded by this choice.